Introduction:
Akin L. Mabogunje is an African Scholar who has approached rural-urban migration from different point of view rather than prevailing approaches.It shows the system approach to rural-urban migration is concerned not only with why people migrate but also with the implications and consequences of the process. This theory is designed to answer why and how a rural individual become a permanent city dweller as well as what factors are operating on the
system. This theory is written with the particular reference to Africa.1. Environment:
Comprises “the set of all objects a change in whose attributes affects the system, and also those objects whose attributes are changed by the behaviour of the system. This is the environment which stimulates the villager to desire change in the basic locale and rationale of his economic activities and which, in consequence, determines the volume, characteristics, and importance of rural-urban migration.
2. System:
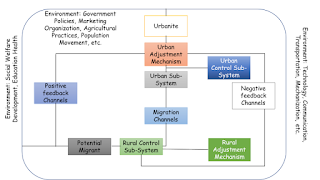
A system may be defined as a complex of interacting elements, together with their attributes and relationships . Figure indicates the basic elements in the rural-urban migration system as well as the environment within which the system operates. It identified first the potential migrant who is being encouraged to migrate from the environment.
3. Sub-System:
. A control sub-system is one which oversees the operation of the general system and determines when and how to increase or decrease the amount of flow in the system.There are two types of sub-system:
I. Rural Sub-System: family structure,age at marriage, age at economic independent, land tuner or holding system,agriculture activities,etc.
II. Urban Sub-System: employment opportunities, residential facilities, urban wages,etc.
The urban control sub-system operates at the opposite end of the migrant’s trajectory to encourage or discourage them from being absorbed into the urban environment. Absorption at this level is of two kinds:
1. Residential
2. Occupational
4. Adjustment Mechanism:
• These are the series of factors in the environment which acts like push or pull factors and operates both the rural and urban sub-system. It is also of two types:
1. Rural Adjustment Mechanism : agriculture production, types of production, income, land tenure system, land distribution and ownership
2. Urban Adjustment Mechanism: socio-economic needs of migrants, own community, ethnic union
Urban adjustment mechanism act both positively or negatively to adjust migrant in the urban sector.
5.Energy:
A system comprises not only matter (the migrant, the institutions,and the various organizations mentioned) but also energy. In the physical sense, energy is the capacity of body to do work. It can be expressed two forms of it which are relevant here :“potential energy’’ which is the body’s power of doing work by virtue of stresses resulting from its relation either with its environment or with other bodies and the second form is “kinetic energy” which is the capacity of a body to do work by virtue of its own motion or activity. In a theory of rural-urban migration:
1. Potential energy can be likened to the stimuli acting on the rural individual to move.
2. Kinetic Energy is translation of potential energy when the individual has been successfully dislodge from the rural area.
Relationship between the System and Environment:
Systems can be classified into three categories depending on the relationship they maintain with their environment;
1. Isolated systems which exchange neither “matter” nor “energy” with their
Environment
2. Closed systems which exchange “energy” but not “matter”;
3. Open systems which exchange both “energy” and “matter”